Describe the Anatomy and Histology of Bone Tissue
In this short article I am going to describe. Once ossification becomes apparent in the epiphyses then the bone is in stage 2 of development.
Seer Training Structure Of Bone Tissue
Stage 4 represents complete fusion.

. Later discussions in this chapter will show that bone is also dynamic in that its shape adjusts to accommodate stresses. Osteoblasts are bone-forming cell osteoclasts resorb or break down bone and osteocytes are mature bone cells. The aim of this paper was to present and describe standardized terminology used in histologic and histomorphometric analysis of bone tissue.
The organic component is largely Type I collagen and ground substance collectively this is called osteoid. This section will examine the gross anatomy of bone first and then move on to its histology. Histology of bone.
Bone is hard and many of its functions depend on that characteristic hardness. Gross Anatomy of Bone. Cartilage is thin avascular flexible and resistant to compressive forces.
Bones articulate with other bones by way of joints which can be synovial. Bone tissue osseous tissue differs greatly from other tissues in the body. Bone Formation Growth.
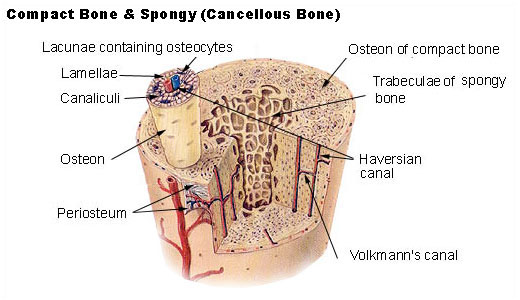
These lamellae of the bony matrix consist of lacunae which contain osteocytes. -collagen proteins -crystalline salts of calcium. In this review we provide an overview on the anatomy and histology of the male skeleton also highlighting the main differences with the female one during growth and adulthood.
Histology of bone. Bone Matrix and Cells Bone Matrix Osseous tissue is a connective tissue and like all connective tissues contains relatively few cells and large amounts of extracellular matrix. Bone tissue is the structural component of bones.
This section will examine the gross anatomy of bone. Figure 633 Anatomy of a Flat Bone. The solid extracellular bone _____ is made of.
Bone is hard. Bone tissue osseous tissue differs greatly from other tissues in the body. In this anatomy course part of the Anatomy Specialization you will learn how the components of the integumentary system help protect our body epidermis dermis hair nails and glands and how the musculoskeletal system bones joints and skeletal muscles protects and allows the body to move.
Here we see the microscopic structure of bones that contains an extracellular matrix that surrounds cells. Bone is primarily composed of extracellular matrix with organic and inorganic components. Bone tissue formation.
It is the nature of the matrix that defines the properties of these connective tissues. Type of tissue composed of cells osteocytes osteoblasts osteoclasts osteoprogenitors and a solid extracellular matrix. Structure of Bone Tissue.
Each trabecula of the spongy bone is made of several parallel lamellae of the bony matrix. Bone is a special connective tissue that contains cells fibres ground substances and inorganic bone salts. Non collagenous proteins that contribute to osteoid include growth factors glues and proteins that help to initiate mineralization.
From a histological point of view it is composed of a dense homogeneous extracellular matrix which is mineralized for the most part and by bone cells osteoblasts osteocytes and osteoclasts that are devoted to its formation and its remodeling. Later discussions in this chapter will show that bone is also dynamic in that its shape adjusts to accommodate stresses. The fundamental components of bone like all connective tissues are cells and matrix.
Up to 24 cash back - describe the anatomy and histology of bone tissue SC912L1413 - distinguish between bones of the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton SC912L1414 - identify the major bones of the axial and appendicular skeleton. Introduction Bone tissue along with other CT like cartilage fibrous tissue fat blood vessels nerves and hematopoietic elements form the individual bones. The names imply that the two types differ in density or how tightly the tissue is packed together.
The musculoskeletal system consists of hard tissues bones joints cartilage and soft tissues muscles tendons ligaments. Compact Bone Histology Circumferential Interstitial and Haversian System. They are both made up of cells embedded in an extracellular matrix.
Describe the anatomy and histology of bone tissue. The diaphysis and the epiphysisThe diaphysis is the tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. Bones are the organs of the skeletal system.
You will find the marrow space between the trabeculae in the spongy bone structure. Histology of the bone. This cross-section of a flat bone shows the spongy bone diploë covered on either side by a layer of compact bone.
Histologic analysis of bone tissue specimen provides an insight in the features and quality of cellular activities. At the point where the epiphyses and diaphysis begin to fuse then the bone has entered stage 3. Bone tissue is characterized by specific activities which are the result of cell function throughout life.
Bone is a tissue in which the extracellular matrix has been hardened to accommodate a supporting function. In bone you will find two types of substances compact and spongy substances. Cartilage and Bone are specialised forms of connective tissue.
In stage 1 the epiphysis is not yet ossified. 03042021 21032021 by anatomylearner. Bone tissue is a specialized type of connective tissue that contains cells osteoblasts osteocytes osteoclasts fibers collagen type I and mineralized extracellular matrix.
21 rows Bone tissue osseous tissue differs greatly from other tissues in the body. Anatomy and Physiology 2 Final Exam Study Guide--Mulitple Choice. Bone is a mineralized connective tissue that exhibits four types of cells.
These marrow spaces contain blood vessels and hemopoietic tissue. Enroll for Free. There are two types of bone tissue.
There are three key cells of bone tissue. Bone is hard and many of its functions depend on that characteristic hardness. The structure of a long bone allows for the best visualization of all of the parts of a bone A long bone has two parts.
Osteoblasts bone lining cells osteocytes and osteoclasts 1 2. Bone exerts important functions in the body such as locomotion support and protection of soft tissues calcium and phosphate storage and harboring of bone marrow 3 4. There are three types of cells that contribute to bone homeostasis.
We also describe the specific mechanisms of sexual hormones on bone cells and the pathological consequences caused by their deficiency on skeletal homeostasis. The extracellular matrix consists of about 15 water 30 collagen fibers and 55 crystallized mineral salts like calcium phosphate these then combines with another mineral salt calcium. They each have unique functions and are derived from two different cell lines.
Posted on June 13 2019.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1893/LMWu67nPEjziY7G5yghKdw_histology-bone-tissue-formation_english.jpg)
Bone Histology Constituents And Types Kenhub

Endosteum Definition Function Histology Vs Periosteum Anatomy Bones Skeletal System Anatomy Bones Human Body Projects

Principles Of Anatomy And Physiology Chapter 6 The Skeletal System Bo Anatomy And Physiology Book Basic Anatomy And Physiology Skeletal System Anatomy Bones
Comments
Post a Comment